Middle ear infections, or otitis media, are common in children and can cause discomfort and worry for parents. At Heart & Soul Integrative Health, we focus on holistic and integrative approaches to managing these infections while ensuring the best outcomes for your child.
What Is Otitis Media?
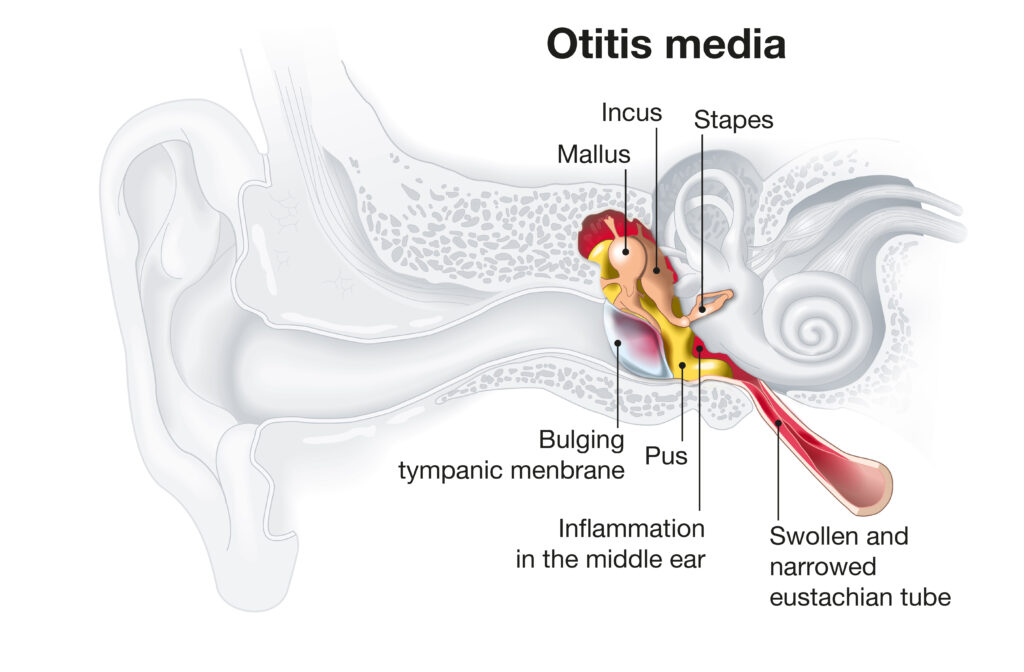
A middle ear infection involves ear pain and sometimes a fever, typically following a common cold or respiratory infection. During an ear exam with an otoscope, a true infection will show signs of inflammation or fluid in the middle ear.
While antibiotics are often recommended for true middle ear infections, some symptoms may be due to congestion in the middle ear rather than an infection. In such cases, watching and waiting might be advised, alongside natural remedies to relieve symptoms.
Natural Remedies for Middle Ear Discomfort
If symptoms are due to middle ear fluid rather than an infection, the following remedies may help alleviate discomfort:
- Onion Compress:
- Use a room-temperature onion, cut it in half, and slice one piece from each half.
- Wrap each slice in gauze or cheesecloth and place it over each ear.
- Secure in place with gauze, cheesecloth, or a fitted cloth cap, and leave the compress on for as long as possible, ideally overnight.
- This method helps relieve ear pain and discomfort naturally.
- Ear Relief Drops:
- Over-the-counter drops containing chamomilla, sulphur, and mercurius can provide pain relief.
- Important: Avoid using drops if there is any ear drainage.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of otitis media can be managed naturally, it’s important to recognize when professional care is needed. Contact your provider if:
- Antibiotics were started, but fever over 100.4°F persists after 48 hours.
- There is ear drainage.
- Pain worsens or a new fever develops after deciding not to use antibiotics.
- Redness, swelling, or pain appears behind the ear.
- The outer ear appears swollen or propped forward.
What is the difference between middle ear fluid and a true ear infection?
Middle ear fluid is often caused by congestion following a cold or respiratory infection and does not necessarily indicate an infection. A true ear infection involves inflammation or bacteria in the middle ear, often requiring antibiotics.
How can I tell if my child has a middle ear infection?
Signs of a middle ear infection include ear pain, fever, difficulty hearing, and irritability. A doctor can confirm the diagnosis with an otoscope examination.
Can I use home remedies for an ear infection?
Home remedies like onion compresses and ear drops can help relieve symptoms but will not treat an active bacterial infection. Always consult with a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen.
Should I avoid antibiotics for my child’s ear infection?
In some cases, a watch-and-wait approach may be recommended if symptoms are mild. However, true bacterial infections typically require antibiotics to prevent complications.
Are natural remedies safe for children?
Yes, remedies like onion compresses and over-the-counter ear drops are generally safe when used as directed. Avoid using drops if there is ear drainage, and always monitor for worsening symptoms.
When should I take my child to the doctor for an ear infection?
You should seek medical attention if your child has:
- A fever over 100.4°F lasting more than 48 hours after starting antibiotics.
- Ear drainage.
- Worsening pain or a new fever.
- Redness, swelling, or pain behind the ear.
Supporting Your Child Holistically
At Heart & Soul Integrative Health, our priority is to empower families with personalized, holistic care that aligns with their values and beliefs. Whether it’s offering practical guidance on natural remedies or providing clarity on when antibiotics are necessary, we’re here to ensure your child’s health and well-being are supported every step of the way.
Our integrative approach combines the best of traditional and holistic medicine, creating tailored care plans that address your child’s unique needs while respecting your parenting choices.
A middle ear infection involves ear pain and sometimes fever, usually following a cold or respiratory infection. It is confirmed by a doctor using an otoscope to check for inflammation or fluid in the middle ear.
Middle ear fluid is often caused by congestion after a cold and does not necessarily indicate an infection. A true ear infection involves inflammation or bacteria and often requires antibiotics.
Home remedies, like onion compresses and over-the-counter ear relief drops, can help alleviate symptoms. However, these remedies do not treat bacterial infections. Consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen.
An onion compress can naturally relieve ear pain by soothing discomfort caused by middle ear fluid. To use, wrap a room-temperature onion slice in gauze, place it over the ear, and secure it with cloth or gauze.
Yes, remedies like onion compresses and ear drops containing chamomilla, sulphur, and mercurius are generally safe when used as directed. Avoid using ear drops if there is ear drainage, and monitor for worsening symptoms.
In mild cases, a watch-and-wait approach may be appropriate. However, bacterial infections typically require antibiotics to prevent complications. Consult your provider for guidance.
Fever over 100.4°F persists for more than 48 hours after starting antibiotics.
There is ear drainage.
Pain worsens or a new fever develops.
Redness, swelling, or pain appears behind the ear.
The outer ear appears swollen or propped forward.
Heart & Soul Integrative Health provides holistic pediatric care in Marble Falls and Burnet, serving families from across the Texas Hill Country, including Johnson City, Blanco, Kingsland, Llano, Spicewood, Lakeway, Bee Cave, and Austin. Telehealth appointments are available for some concerns. Our integrative approach combines conventional medicine with evidence-based therapies to support your child’s health and well-being.



